Fire Safety Considerations for Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Systems for Tribal Communities
Solar energy is a significant opportunity for Native American communities, providing pathways to energy sovereignty, economic development, and environmental protection. Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems allow tribes to harness clean energy, reduce utility costs, and support sustainability goals. However, it is crucial to address safety challenges, particularly fire safety, to ensure these systems benefit the community without introducing unnecessary risks. Fire safety for solar PV systems must be prioritized by tribal members, tribal councils, and planning and housing departments to ensure safe integration into homes, community buildings, and infrastructure.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore best practices, fire safety standards, installation considerations, and emergency response strategies to mitigate the risk of fires in solar installations. By focusing on these safety measures, tribal communities can ensure that solar PV systems contribute to a clean and sustainable future while protecting lives and property.Understanding Fire Safety in Solar PV Systems
Fire safety is especially important for tribal lands, where the remoteness of many communities can make emergency response times longer and infrastructure more vulnerable. The unique conditions and challenges on tribal lands make it essential to adopt proactive fire safety measures when installing and maintaining solar PV systems. Understanding the potential fire risks and mitigating them is key to protecting both people and property.
The installation of solar photovoltaic (PV) panels on rooftops and properties within tribal lands is becoming increasingly common, but it introduces unique fire safety challenges. The presence of high-voltage DC electricity, combined with various components, can pose a risk if the system is not properly designed, installed, and maintained. Understanding the potential risks and implementing mitigation strategies is key to preventing incidents.Key Fire Risks in Solar PV Installations
Solar PV systems, if not properly managed, can introduce several fire risks. Understanding these risks is essential to creating a safe energy system for tribal communities. Here are some key risks, along with examples of incidents that have occurred due to improper solar PV installations in rural and remote areas.
Best Practices for Fire Safety in Solar PV Systems
To ensure that solar PV systems are safe and do not pose a fire risk, several best practices should be followed during installation, maintenance, and emergency response. These best practices are crucial for reducing risks and ensuring compliance with fire safety regulations.1. Compliance with Codes and Standards
It is essential to adhere to established codes and standards when installing solar PV systems on tribal lands. In addition to national standards such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) and International Fire Code (IFC), tribal regulations and building codes must also be considered. Tribal communities may have specific requirements that interact with these standards, and it is crucial to consult with local authorities to ensure compliance.


The design of the solar PV system plays a significant role in its overall safety. Key considerations include:

Expanding Solar Energy Opportunities for Tribal Communities
Building on the importance of fire safety in solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, tribal communities can explore additional opportunities related to solar energy that further empower their people while ensuring safety, economic growth, and sustainability. Beyond fire safety, it is crucial to consider other facets of solar PV system implementation that can bring broader benefits to Native American tribes, including community engagement, workforce development, financial incentives, and resilience against climate change.
In this continuation, we delve deeper into strategies for maximizing the value of solar PV systems for tribal communities, expanding renewable energy adoption, securing funding, and enhancing community participation.
1. Community Engagement and Solar Energy Awareness
Effective community engagement is essential for successful solar energy adoption. It is crucial for tribal councils and community leaders to actively involve tribal members in the process of transitioning to solar energy. This engagement ensures community buy-in, fosters understanding, and builds trust in the technologies being implemented.
A. Community Meetings and Educational Workshops
B. Solar Demonstration Projects
Implementing solar demonstration projects in visible community areas such as community centers, schools, or health facilities can showcase the benefits of solar energy firsthand. These projects serve as powerful tools for increasing awareness and confidence in solar technologies.
2. Workforce Development and Training Programs
Creating job opportunities through solar projects is an impactful way to support economic development within tribal communities. Workforce development initiatives can provide employment for tribal members, build capacity for future projects, and promote local expertise in solar PV technology.
A. Establishing Local Training Programs
B. Funding Opportunities for Workforce Training
3. Financial Incentives and Funding Opportunities
Financing solar PV projects can be a major barrier, but several funding opportunities and incentives are available specifically for tribal communities. Identifying and leveraging these opportunities can help make solar projects financially viable.
A. Federal and State Grants
B. Tax Credits and Incentives
C. Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) can be a practical way for tribal communities to adopt solar energy without the upfront capital cost. In a PPA, a third-party developer finances, installs, and maintains the solar system, and the tribe agrees to purchase the generated electricity at a predetermined rate. This arrangement can make solar energy
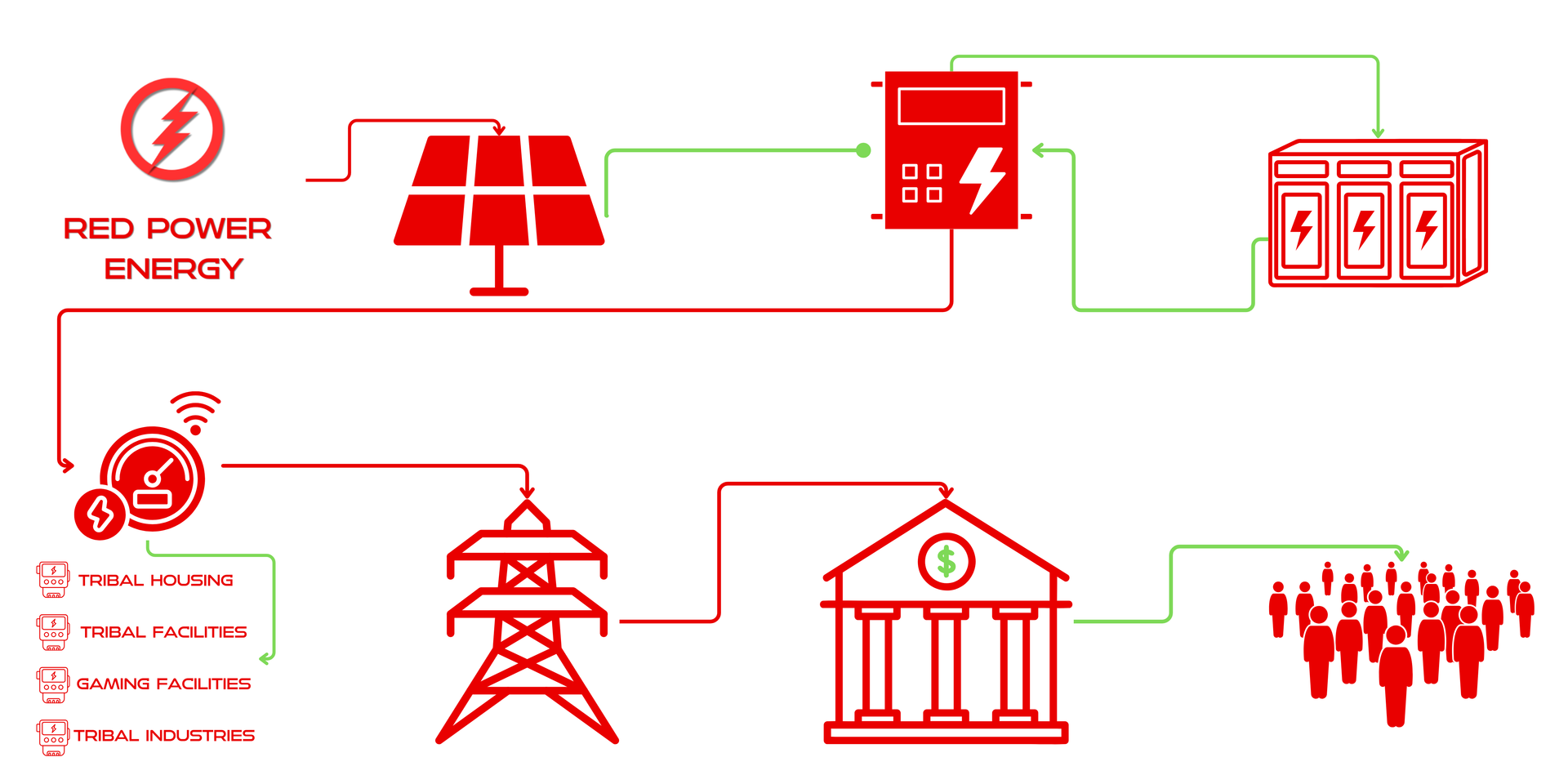
Solar panels absorb
sunlight,
transferring the
energy
to negatively
charged particles
called electrons
creating electricity
It’s a device
that converts direct
current (DC) electricity, which is what
a solar panel
generates,
to alternating
current (AC) electricity, which the electrical
grid uses.
A solar-plus-storage system is a battery system that is charged by a connected solar system, such as a photovoltaic (PV) one.
Net metering is a billing mechanism that credits solar energy system owners for the electricity they add to the grid.
Your unused power can be sold to your traditional electrical provider at competitive rates.
Tribal Leadership can re-invest savings and profit back into education, healthcare, infrastructure and development
Tribal members benefit from lower energy costs, reliable access, and essential utilities during disaster.
• Decrease reliance on fossil fuels
• Contribute to global climate change mitigation efforts
• Set an example for sustainable tribal development
• Protect against power outages and grid failures
• Ensure continuous operation of critical services
• Adapt to changing environmental conditions
• Foster energy independence and self-determination
• Provide opportunities for skill development and education
• Strengthen tribal governance through energy management
Create local jobs in installation, maintenance, and operations
• Attract eco-tourism and green businesses
• Generate revenue through excess energy production
A: Solar energy can provide numerous benefits to your tribe, including:
A: We offer comprehensive solar energy services, including:
Red Power Energy specializes in Native American Renewable Energy with a focus on electrifying tribes. As a !00% Native Owned company, We understand your unique needs, sovereignty issues, and the importance of preserving our cultural heritage while advancing your energy infrastructure.
A: Red Power Energy offers a comprehensive initial consultation where we assess your tribe's energy needs, land resources, and economic goals. We will explain the potential of solar for your specific situation and outline possible project paths and a written offer to assist moving forward.
A: Project timelines can vary depending on size, complexity, and permitting requirements. Generally, smaller projects might take 3-6 months, while larger utility-scale projects could take 12-18 months or more. We work closely with tribal authorities to streamline the process as much as possible.
A: Yes, there are several funding options specifically for tribal solar projects, including:
A: Solar energy systems can work in most climates and locations, even in areas with less direct sunlight. Modern solar panels are efficient and can generate electricity from both direct and indirect sunlight. We conduct thorough site assessments to ensure optimal system design for your specific location.
A: We prioritize cultural sensitivity by:
A: Most solar panel systems have a lifespan of 25-30 years or more. Inverters typically last 10-15 years and may need replacement during the system's lifetime. We offer long-term maintenance plans to ensure your system operates at peak efficiency throughout its lifespan.
A: Solar energy storage, typically using batteries, allows you to store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during cloudy periods. While not always necessary, storage can increase energy independence and resilience, especially in remote areas or regions with unreliable grid power.
A: Yes, tribes can generate revenue through:
A: Solar energy can enhance tribal sovereignty by:
A: Absolutely. Solar energy can support various tribal initiatives, including:
(855)573-3769